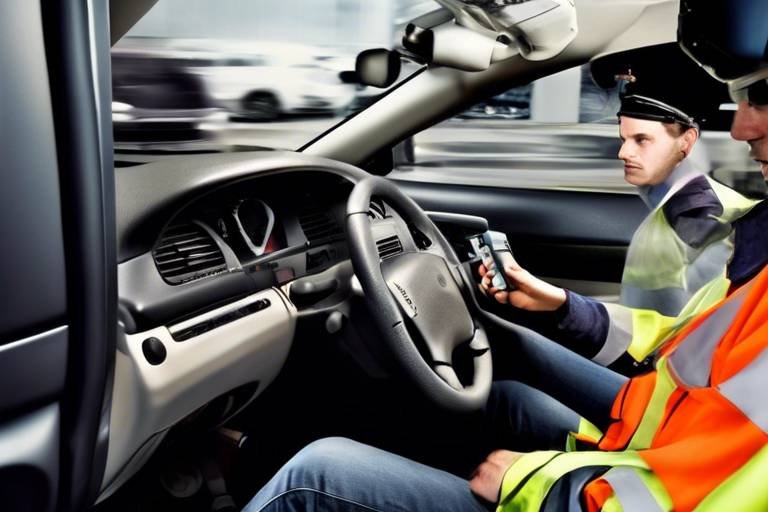
How does Human Behavior affect Your Safety Strategy?
In today's world, where safety is a top priority across various sectors, understanding the intricate relationship between human behavior and safety strategies is more critical than ever. It's not just about having the right protocols in place; it's about how people interact with those protocols. Have you ever wondered why some safety measures are followed diligently while others are ignored? The answer often lies in the psychology behind human behavior. By delving into the cognitive processes that shape our perceptions and decisions regarding safety, organizations can create strategies that resonate more effectively with their teams.
Imagine walking into a workplace where everyone is aware of the safety protocols but few adhere to them. This scenario highlights a fundamental issue: compliance is not merely about rules; it's about understanding the human factors at play. When individuals perceive risks differently, it can lead to inconsistent safety practices. Therefore, addressing these psychological elements can significantly enhance safety protocols and reduce risks in various environments, from corporate offices to construction sites.
To effectively incorporate human behavior into safety strategies, organizations must first acknowledge the psychological aspects of risk perception. Individuals often assess risks based on their experiences, beliefs, and even emotions. This means that two people can look at the same situation and come to vastly different conclusions about the level of risk involved. By recognizing these differences, safety leaders can tailor their approaches to better connect with their teams, ultimately fostering a culture of safety that is both proactive and responsive.
Furthermore, understanding the social dynamics within teams can lead to more effective safety strategies. Group behavior can significantly influence individual actions, either positively or negatively. For example, if a team collectively prioritizes safety, individual members are more likely to follow suit. Conversely, if safety norms are lax, even the most conscientious employees might let their guard down. This interplay between individual and group behavior underscores the importance of not only implementing safety measures but also nurturing an environment where safety is a shared value.
In conclusion, human behavior is a pivotal factor in shaping effective safety strategies. By considering the psychological and social influences that drive individuals' actions, organizations can develop more comprehensive safety protocols that resonate with their employees. This approach not only enhances compliance but also fosters a robust safety culture, ultimately leading to a safer workplace for everyone.
- Why is understanding human behavior important for safety strategies? Understanding human behavior helps organizations tailor safety protocols to fit the psychological and social dynamics of their teams, improving compliance and reducing risks.
- What role do cognitive biases play in safety decisions? Cognitive biases can distort risk perception and decision-making, leading individuals to underestimate dangers or overlook safety measures.
- How can group dynamics affect safety compliance? Group dynamics can enhance or undermine safety compliance; positive peer influence can encourage adherence, while negative group behaviors can lead to complacency.
- What strategies can promote a positive safety culture? Strategies include open communication, recognition of safe behaviors, regular training, and leadership engagement to create a shared commitment to safety.

The Psychology of Risk Perception
When it comes to safety, understanding the psychology of risk perception is absolutely vital. It’s fascinating how our brains process risk—sometimes, they can play tricks on us! Most people think they have a good grip on what’s dangerous and what isn’t, but the truth is, our perceptions are often skewed by various factors. Have you ever felt more anxious about flying than driving, even though statistically, flying is safer? This discrepancy is a classic example of how cognitive biases can warp our understanding of risk.
One of the key elements influencing risk perception is our cognitive biases. These are systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. For instance, the availability heuristic leads us to overestimate risks that we readily recall, often based on recent news stories or personal experiences. If you hear about a plane crash, you might irrationally think flying is more dangerous, even if the statistics say otherwise. On the flip side, we might underestimate risks that are less sensationalized, like the dangers of texting while driving.
Another factor is the optimism bias, which makes us believe that we are less likely to experience negative events compared to others. This can lead to complacency in safety practices. For example, someone might think, “I’m a great driver; I’ll never get into an accident,” which can result in risky behaviors like speeding or distracted driving. The irony is that while we believe we’re invulnerable, the reality often tells a different story.
To illustrate how these biases manifest in real-world situations, consider the following table that outlines some common cognitive biases related to risk perception:
| Cognitive Bias | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Availability Heuristic | Overestimating the likelihood of events based on recent memories. | Fear of flying after hearing about a plane crash. |
| Optimism Bias | Believing that one is less likely to experience a negative event than others. | Thinking “I won’t get caught speeding” despite frequent violations. |
| Confirmation Bias | Seeking information that confirms existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory data. | Only reading articles that support the idea that a particular safety measure is unnecessary. |
Understanding these biases is not just an academic exercise; it has real implications for safety strategies in workplaces and communities. By recognizing how these cognitive distortions affect decision-making, organizations can tailor their safety protocols to address these psychological factors. For instance, incorporating regular training sessions that highlight the importance of safety, regardless of personal beliefs, can help mitigate the effects of optimism bias.
Moreover, awareness programs can also educate individuals about the availability heuristic. When people understand that their perceptions may be influenced by recent events, they can learn to evaluate risks more objectively. This can lead to better decision-making and ultimately enhance safety compliance across various environments.
In conclusion, the psychology of risk perception is a complex but critical area of study for anyone involved in safety strategy development. By addressing cognitive biases and fostering a culture of awareness, we can significantly improve the effectiveness of safety measures and ultimately save lives. So, the next time you think about risk, take a moment to reflect—are your perceptions truly aligned with reality?

When it comes to safety, our decisions are often influenced by a myriad of factors, many of which stem from cognitive biases. These biases are like invisible glasses that tint our perception of risk and safety, often leading us to make choices that may not align with reality. For instance, optimism bias is a common phenomenon where individuals believe that they are less likely to experience negative events compared to others. Imagine a worker who thinks, "Accidents happen to others, but not to me." This mindset can lead to complacency, increasing the likelihood of unsafe behaviors.
Another significant bias is confirmation bias, where individuals tend to seek out information that supports their pre-existing beliefs while ignoring evidence to the contrary. In a safety context, this could manifest when a manager disregards data showing a rise in incidents because it contradicts their belief that their team is operating safely. Such biases can create a dangerous disconnect between perception and reality, ultimately undermining safety protocols.
Moreover, cognitive biases can also affect how safety information is communicated within organizations. For example, if employees are accustomed to hearing only positive feedback about their safety practices, they may become less vigilant. This is where the role of effective communication becomes crucial. Organizations must strive to present data in a way that encourages critical thinking and reflection, rather than simply reinforcing existing beliefs.
To combat these biases, organizations can implement training programs that specifically address cognitive distortions. By educating employees about these biases, they can become more aware of their thought processes and learn to question their assumptions. For example, training sessions could include scenarios that challenge optimistic views or encourage employees to critically assess their safety practices. This proactive approach not only enhances awareness but also fosters a culture of safety where individuals feel empowered to speak up about potential risks.
In addition, it’s essential to create an environment where open dialogue is encouraged, allowing employees to share concerns without fear of retribution. When people feel safe to express their thoughts, it can lead to a collective reassessment of safety practices, ultimately leading to improved outcomes. After all, safety is not just about policies and procedures; it's about the people who implement them.
In conclusion, recognizing and addressing cognitive biases in safety decisions is vital for organizations aiming to enhance their safety culture. By fostering awareness and encouraging open communication, companies can mitigate the effects of these biases, leading to more informed decision-making and ultimately a safer workplace.
- What are cognitive biases? Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, which can affect decision-making.
- How do cognitive biases impact safety decisions? They can lead to overconfidence, misinterpretation of data, and a lack of critical assessment of safety practices.
- What can organizations do to mitigate cognitive biases? Organizations can implement training programs that educate employees about these biases and encourage open communication regarding safety concerns.

When it comes to safety compliance, group dynamics play a crucial role in shaping behaviors and attitudes within an organization. Think about it: when you’re part of a team, your actions are often influenced by those around you. This phenomenon is known as social influence, and it can significantly affect how seriously safety protocols are followed. For instance, if your coworkers are lax about wearing protective gear, you might feel tempted to follow suit, even if you know the risks. This tendency can lead to a culture where safety becomes an afterthought rather than a priority.
Moreover, the concept of peer pressure extends beyond just teenagers in high school; it’s a powerful force in the workplace too. Employees may feel pressured to conform to the norms established by their peers, which can either enhance or undermine safety practices. For example, if a team consistently skips safety briefings because “everyone else does,” new members might feel compelled to do the same, regardless of their own safety concerns. This underscores the importance of fostering a strong safety culture where compliance is not only encouraged but celebrated.
Another critical aspect of group dynamics is groupthink. This psychological phenomenon occurs when the desire for harmony or conformity in a group results in irrational or dysfunctional decision-making. When it comes to safety, groupthink can lead to dangerous oversights. Teams may overlook safety hazards simply because no one wants to rock the boat or challenge the status quo. To combat this, it's essential to create an environment where individuals feel safe to voice concerns and suggest improvements without fear of backlash.
So, how can organizations enhance safety compliance through understanding group dynamics? Here are a few strategies:
- Encourage Open Communication: Create channels where employees can express their concerns and suggestions regarding safety without fear of judgment.
- Promote Accountability: Foster a sense of responsibility among team members. When everyone feels accountable for safety, compliance improves.
- Recognize and Reward Safe Behavior: Implement recognition programs that highlight employees who exemplify safe practices, reinforcing positive behavior within the group.
By addressing these dynamics, organizations can significantly enhance their safety compliance. It’s about shifting the focus from individual responsibility to collective accountability, ensuring that everyone understands their role in maintaining a safe work environment. Ultimately, when safety becomes a shared value, the entire organization benefits, leading to reduced risks and a healthier workplace.
- What is group dynamics in the context of safety? Group dynamics refer to the behavioral and psychological processes that occur within a social group, influencing how members interact and comply with safety protocols.
- How can peer pressure affect safety compliance? Peer pressure can lead individuals to conform to unsafe behaviors if the group norms do not prioritize safety, potentially increasing the risk of accidents.
- What is groupthink and how does it relate to safety? Groupthink is a psychological phenomenon where the desire for group harmony leads to poor decision-making, often resulting in overlooking safety concerns.
- What strategies can improve safety compliance in teams? Strategies include fostering open communication, promoting accountability, and recognizing safe behavior among team members.

Creating a positive safety culture within an organization is not just a checkbox on a compliance list; it's a vital aspect of operational success. Imagine a workplace where every employee feels responsible for their safety and the safety of their colleagues. This kind of environment fosters trust, communication, and ultimately leads to reduced incidents and accidents. So, how do we cultivate such a culture? It starts with open dialogue and a commitment from leadership to prioritize safety as a core value.
One effective strategy to encourage a positive safety culture is to implement regular safety meetings that are not just routine but engaging. These meetings should encourage employees to share their experiences, insights, and suggestions regarding safety practices. When employees feel their voices are heard, they are more likely to take ownership of their roles in maintaining a safe environment. Moreover, recognizing individuals or teams who demonstrate exceptional safety practices can further motivate others to follow suit.
Another crucial element is to provide comprehensive and accessible safety training. This training should not be a one-time event but rather an ongoing process that evolves with the organization. Utilizing various training methods, such as interactive workshops and online modules, can cater to different learning styles. For instance, scenario-based training allows employees to engage in realistic situations, enhancing their preparedness for real-life emergencies. This hands-on approach not only reinforces the importance of safety but also builds confidence in their ability to respond effectively.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of accountability is essential. Employees should understand that safety is a shared responsibility, and everyone plays a role in it. This can be achieved by establishing clear expectations and guidelines regarding safety practices. When individuals know they are accountable for their actions, they are more likely to adhere to safety protocols. It's also important to create an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting unsafe conditions or behaviors without fear of reprimand. Encouraging this type of transparency can lead to proactive measures that prevent accidents before they happen.
Lastly, leadership plays a pivotal role in shaping a positive safety culture. Leaders must not only advocate for safety but also model safe behaviors themselves. When employees see their leaders prioritizing safety, it sends a strong message about its importance. Engaging with employees on the ground level, participating in safety drills, and being approachable for safety discussions can significantly enhance the perception of safety within the organization.
In conclusion, encouraging a positive safety culture requires a multifaceted approach that includes open communication, ongoing training, accountability, and strong leadership. By embedding these principles into the organizational fabric, companies can create a safer workplace where employees feel empowered and committed to maintaining high safety standards.
- What is a safety culture? A safety culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, and practices within an organization that prioritize safety and well-being.
- How can leadership influence safety culture? Leaders can influence safety culture by modeling safe behaviors, communicating the importance of safety, and engaging employees in safety initiatives.
- What are some effective training methods for safety? Effective training methods include scenario-based training, interactive workshops, and ongoing online modules that cater to different learning preferences.
- Why is employee involvement important in safety culture? Employee involvement fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, leading to a more proactive approach to safety and reduced incidents.

Leadership is not just about making decisions; it's about influencing and inspiring others to adopt safe practices. When it comes to safety behavior, the role of leaders is paramount. Strong leaders set the tone for safety culture within an organization, and their actions often speak louder than words. Have you ever wondered why some teams consistently adhere to safety protocols while others seem to overlook them? The answer often lies in the leadership style and commitment to safety demonstrated by their supervisors.
Leaders who prioritize safety create an environment where employees feel valued and protected. This can significantly impact their willingness to comply with safety measures. For instance, when leaders actively participate in safety training sessions, it sends a powerful message that safety is a shared responsibility. Employees are more likely to follow suit when they see their leaders engaging in the same practices they are asked to uphold.
Moreover, effective communication plays a crucial role in shaping safety behavior. Leaders who communicate openly about safety concerns and encourage feedback create a culture of trust. This transparency allows employees to voice their worries without fear of reprimand, fostering a proactive approach to safety. When leaders listen to their team members, they not only gain valuable insights but also empower employees to take ownership of their safety practices.
To illustrate the impact of leadership on safety behavior, consider the following table that outlines the key characteristics of effective safety leadership:
| Leadership Trait | Description |
|---|---|
| Visibility | Leaders should be present in the workplace, demonstrating their commitment to safety. |
| Communication | Open dialogue about safety issues encourages a culture of transparency and trust. |
| Accountability | Taking responsibility for safety outcomes fosters a sense of ownership among employees. |
| Recognition | Recognizing and rewarding safe behavior reinforces positive practices. |
In addition to these traits, leaders must also be aware of their own behavior and the messages it conveys. For example, if a leader consistently ignores safety protocols, employees may perceive safety as a low priority. Conversely, when leaders model safe behavior, they create a ripple effect throughout the organization. Employees are more likely to adopt similar behaviors, leading to a safer work environment overall.
Moreover, leadership training focused on safety can help equip leaders with the necessary skills to foster a positive safety culture. Training can include topics such as effective communication, conflict resolution, and crisis management. By investing in leadership development, organizations can ensure that their leaders are prepared to handle safety challenges effectively.
Ultimately, the impact of leadership on safety behavior cannot be overstated. Leaders who are committed to safety not only protect their employees but also enhance overall organizational performance. A strong safety culture leads to fewer accidents, reduced costs, and improved employee morale. So, the next time you think about safety in your organization, remember that it starts at the top. Are your leaders leading by example?
- What is the role of leadership in promoting safety? Leadership plays a crucial role in setting the tone for safety culture and influencing employee behavior.
- How can leaders improve safety compliance among employees? By actively participating in safety initiatives, communicating openly, and recognizing safe behaviors.
- What characteristics should effective safety leaders possess? Visibility, communication skills, accountability, and the ability to recognize and reward safe practices.
- Why is training important for leaders in safety management? Training equips leaders with the skills needed to foster a positive safety culture and effectively manage safety challenges.

When it comes to safety behavior, it's essential to recognize that not everyone reacts the same way in various situations. Individual differences, such as personality traits, past experiences, and even cultural backgrounds, play a significant role in shaping how people approach safety protocols. For instance, a person with a high level of conscientiousness—often characterized by being organized, responsible, and diligent—is likely to adhere strictly to safety guidelines. In contrast, someone who scores lower on this trait may exhibit a more relaxed attitude towards safety, potentially putting themselves and others at risk.
Moreover, past experiences can greatly influence an individual's perception of risk and safety behavior. Someone who has previously encountered a dangerous situation may be more vigilant and cautious, while another person who has never faced such a scenario might underestimate the risks involved. This disparity in experiences can lead to a wide range of responses to safety protocols, which can be problematic in environments where uniform compliance is necessary.
Additionally, cultural factors can also contribute to individual differences in safety behavior. In some cultures, there is a strong emphasis on collective responsibility and community well-being, which can foster a heightened sense of safety awareness. Conversely, in cultures that prioritize individualism, people might be more inclined to take risks or disregard safety measures, believing that their personal choices should take precedence. Understanding these cultural nuances is crucial for organizations aiming to create effective safety strategies that resonate with their diverse workforce.
To illustrate these concepts, consider the following table that outlines how different personality traits can impact safety behavior:
| Personality Trait | Impact on Safety Behavior |
|---|---|
| Conscientiousness | Higher adherence to safety protocols, thoroughness in following guidelines. |
| Openness to Experience | May encourage innovative safety solutions but could lead to risk-taking if not managed. |
| Neuroticism | Higher anxiety levels may lead to over-cautious behavior, potentially causing delays in decision-making. |
| Agreeableness | Often promotes teamwork in safety initiatives but may lead to conformity at the expense of critical thinking. |
Understanding these individual differences is not just an academic exercise; it's a practical necessity for organizations aiming to enhance their safety strategies. By recognizing that employees bring their unique perspectives and experiences to the table, companies can tailor their safety training and protocols to better suit the diverse needs of their workforce. This could involve personalized training sessions, mentorship programs, or even creating safety committees that reflect a variety of viewpoints.
In conclusion, acknowledging individual differences in safety behavior is crucial for developing effective safety strategies. By leveraging this understanding, organizations can foster a culture of safety that not only complies with regulations but also resonates with employees on a personal level. This approach not only enhances safety compliance but also contributes to a more engaged and proactive workforce.
- What are the main factors that influence individual differences in safety behavior?
Individual differences in safety behavior are influenced by personality traits, past experiences, and cultural backgrounds. - How can organizations address these individual differences?
Organizations can tailor safety training and protocols to accommodate diverse perspectives and experiences among employees. - Why is understanding individual differences important for safety strategies?
Recognizing individual differences helps create a more effective and engaging safety culture, leading to better compliance and risk management.

When it comes to safety, training is not just a formality; it's a fundamental pillar that shapes human behavior in critical situations. Imagine a firefighter who has never practiced putting out a fire. The first time they face a blaze, their chances of success are slim. This analogy underscores the importance of effective training in ensuring that individuals are prepared to handle emergencies. Training provides the necessary knowledge and skills, but it's also about instilling the right mindset towards safety.
Moreover, the effectiveness of training programs is heavily influenced by how they resonate with the participants. If the training is dry and uninspiring, it’s likely to fall on deaf ears. On the contrary, engaging and interactive training sessions can significantly boost participants' interest and retention of safety information. This is where understanding human behavior becomes crucial. By tapping into the psychological factors that motivate individuals, organizations can design training that not only informs but also inspires.
One effective approach is incorporating scenario-based training, which immerses participants in realistic situations that they might face in their work environment. This method allows individuals to practice their responses to potential hazards in a controlled setting. For example, a construction company might simulate a fall from height scenario, giving workers the chance to practice their safety protocols. The result? Enhanced decision-making skills and improved confidence when faced with real-life emergencies.
Furthermore, motivational factors play a significant role in how individuals engage with safety training. Understanding what drives people can lead to more successful training outcomes. Here are some key motivators:
- Intrinsic Motivation: This involves personal satisfaction and a sense of accomplishment that comes from mastering safety skills.
- Extrinsic Motivation: External rewards, such as recognition or incentives, can also encourage participation in safety training.
By addressing both intrinsic and extrinsic motivators, organizations can create a more compelling training environment. For instance, offering certificates or rewards for completing safety courses can provide that extra push for employees to engage actively. Additionally, creating a culture where safety is celebrated can foster intrinsic motivation, making employees feel valued for their commitment to safety practices.
In conclusion, training is a vital component in shaping human behavior towards safety. By understanding and leveraging the psychological aspects of learning and motivation, organizations can enhance their safety protocols and ensure that employees are not just compliant but genuinely committed to maintaining a safe working environment. Whether through engaging scenario-based training or recognizing individual motivators, the goal remains the same: to cultivate a workforce that prioritizes safety in every action.
- What is scenario-based training? Scenario-based training involves creating realistic situations that employees might encounter in their work environment, allowing them to practice their responses in a safe setting.
- Why is motivation important in safety training? Motivation influences how engaged individuals are in training programs, impacting their retention of safety knowledge and their willingness to apply it in real-world situations.
- How can organizations foster a culture of safety? Organizations can foster a culture of safety by recognizing and rewarding safe behaviors, providing engaging training, and ensuring open communication about safety practices.

Scenario-based training (SBT) is a powerful tool in enhancing safety preparedness, especially when it comes to real-life situations. Imagine being in a high-pressure environment where every second counts; how would you react? This is where SBT shines, as it immerses participants in realistic scenarios that mimic actual emergencies. By creating a safe space for individuals to practice their responses, organizations can significantly improve decision-making skills and response times during crises.
One of the main advantages of scenario-based training is its ability to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Traditional training methods often rely heavily on lectures and presentations, which can lead to a disconnect between what employees learn and how they apply that knowledge in real situations. In contrast, SBT engages participants by placing them in simulated environments where they must think critically and act decisively. This hands-on approach not only enhances learning retention but also builds confidence among employees, making them feel more prepared to handle emergencies.
Research has shown that individuals who undergo scenario-based training are better equipped to recognize potential hazards and respond appropriately. For instance, a study conducted in a manufacturing setting revealed that employees who participated in SBT were 40% more likely to identify safety risks compared to those who received conventional training. This improvement can be attributed to the immersive nature of SBT, which encourages participants to actively engage with the material and apply their knowledge in a practical context.
Moreover, SBT fosters teamwork and communication among employees. When faced with a simulated crisis, individuals must collaborate and share information to navigate the situation effectively. This aspect of training not only enhances safety preparedness but also strengthens interpersonal relationships within teams. As employees learn to rely on one another during training, they are more likely to carry that collaborative spirit into their daily work, ultimately contributing to a safer workplace environment.
To illustrate the effectiveness of scenario-based training, consider the following table that compares traditional training methods with scenario-based approaches in terms of key outcomes:
| Training Method | Knowledge Retention | Real-World Application | Team Collaboration | Confidence Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Training | Moderate | Low | Minimal | Low |
| Scenario-Based Training | High | High | High | High |
In conclusion, scenario-based training is not just an educational tool; it is a transformative approach that can significantly enhance safety protocols within an organization. By immersing employees in realistic situations, SBT not only improves their ability to handle emergencies but also fosters a culture of safety and teamwork. As organizations continue to prioritize safety, investing in scenario-based training will undoubtedly yield substantial benefits in risk management and employee preparedness.
- What is scenario-based training?
Scenario-based training is an educational approach that uses realistic simulations to prepare individuals for real-world situations, particularly in emergency response and safety protocols.
- How does scenario-based training improve safety?
It enhances safety by allowing participants to practice their responses in a controlled environment, thereby increasing knowledge retention, confidence, and teamwork skills.
- Is scenario-based training effective for all types of organizations?
Yes, it can be tailored to fit various industries and organizational needs, making it a versatile training method.
- How can organizations implement scenario-based training?
Organizations can collaborate with training professionals to design specific scenarios that reflect potential risks and challenges relevant to their operations.

When we talk about safety training, it’s not just about the rules and regulations; it’s also about understanding what drives people to engage with these crucial programs. Motivational factors are the invisible threads that weave through the fabric of effective safety training. Without them, even the best-designed programs can fall flat. So, what really motivates individuals to take safety training seriously? Let’s dive into some key factors that can make a significant difference.
First and foremost, intrinsic motivation plays a vital role. This refers to the internal desire to perform a task for its own sake. For instance, an employee might engage in safety training because they genuinely care about their own well-being and that of their colleagues. They understand that safety training is not just a checkbox on a to-do list but a way to create a safer work environment. This intrinsic motivation can lead to a more profound commitment to safety practices.
On the flip side, we have extrinsic motivation, which involves external rewards or pressures. These can include incentives such as bonuses, recognition, or even promotions tied to safety performance. Organizations can leverage these external motivators to encourage participation in safety training. For example, a company could implement a reward system where employees who complete safety training earn points that can be redeemed for various perks. This not only boosts participation but also fosters a competitive spirit among employees to prioritize safety.
Moreover, the relevance of training cannot be overstated. When employees see how safety training directly applies to their daily tasks, they are more likely to engage fully. Training that includes real-life scenarios and practical applications can significantly enhance motivation. If employees understand that the training is relevant to their specific roles and can help them avoid potential hazards, they’re much more likely to take it seriously. For instance, a construction worker would find a safety training session on fall prevention much more engaging than a generic session on workplace safety.
Additionally, peer influence can play a crucial role in motivating individuals to participate in safety training. When employees see their peers actively engaging in safety protocols and training, it creates a culture of safety within the organization. This social proof can encourage others to follow suit, as no one wants to feel left out or be perceived as neglecting their responsibilities. Organizations can foster this environment by highlighting success stories and celebrating those who excel in safety practices.
Finally, the quality of the training program itself is a significant motivator. Engaging, interactive, and well-structured training sessions can capture attention and maintain interest. For example, using multimedia elements like videos, quizzes, and group activities can make the learning experience much more enjoyable. A dull, monotonous presentation is likely to lose participants' interest quickly, whereas an interactive session can keep them engaged and motivated to learn.
In summary, understanding the motivational factors behind safety training is essential for creating effective programs. By focusing on intrinsic and extrinsic motivators, ensuring the relevance of training, leveraging peer influence, and enhancing the quality of the training experience, organizations can significantly boost participation and retention of safety knowledge. It’s not just about compliance; it’s about cultivating a culture where safety is a shared value and responsibility.
- What are intrinsic and extrinsic motivators in safety training?
Intrinsic motivators are internal drives to engage in safety training for personal satisfaction, while extrinsic motivators are external rewards or pressures that encourage participation. - How can organizations enhance the relevance of safety training?
By tailoring training sessions to include real-life scenarios and practical applications relevant to employees' specific roles. - Why is peer influence important in safety training?
Peer influence creates a culture of safety where employees are motivated to participate and comply with safety protocols by observing their colleagues' behaviors. - What role does training quality play in motivation?
High-quality, engaging training programs capture attention and maintain interest, leading to higher participation and retention of safety knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does human behavior influence safety strategies?
Human behavior plays a crucial role in shaping safety strategies. Understanding how individuals perceive risk, respond to safety protocols, and interact with their environment can significantly enhance the effectiveness of safety measures. By considering psychological factors, organizations can develop tailored strategies that resonate with employees, leading to better compliance and reduced risks.
- What are cognitive biases, and how do they affect safety decisions?
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment, which can heavily influence safety decisions. For instance, optimism bias may lead individuals to underestimate risks, while confirmation bias can cause them to disregard information that contradicts their beliefs. Recognizing these biases is essential for organizations to create more effective safety practices and training programs.
- How do group dynamics impact safety compliance?
Group dynamics can have a profound impact on safety compliance. Social influences, such as peer pressure and groupthink, can either encourage adherence to safety protocols or lead to their neglect. Understanding these dynamics allows organizations to foster a culture where safety is prioritized and supported by all team members, ultimately enhancing overall safety performance.
- What strategies can promote a positive safety culture?
Promoting a positive safety culture involves several strategies, including open communication, recognition of safe behaviors, and providing ongoing training. Encouraging employees to voice concerns and share experiences fosters a sense of ownership over safety. Additionally, leadership commitment to safety can inspire teams to prioritize safe practices in their daily activities.
- How does leadership affect employee safety behavior?
Effective leadership is pivotal in shaping employee safety behavior. Leaders who actively demonstrate a commitment to safety and engage with their teams can inspire a culture of compliance and accountability. When employees see their leaders prioritizing safety, they are more likely to adopt similar attitudes and behaviors, creating a safer work environment.
- What role do individual differences play in safety behavior?
Individual differences, such as personality traits and past experiences, can significantly influence safety behavior. For example, someone with a high level of conscientiousness may be more diligent about following safety protocols. By understanding these differences, organizations can tailor their safety strategies to address the unique needs and behaviors of their workforce.
- How effective is scenario-based training for safety preparedness?
Scenario-based training is highly effective for enhancing safety preparedness. By simulating real-life situations, employees can practice decision-making and responses in a controlled environment. This hands-on approach not only improves their skills but also boosts confidence, making them better equipped to handle emergencies when they arise.
- What motivates individuals to participate in safety training?
Motivational factors for participating in safety training can be categorized into intrinsic and extrinsic motivators. Intrinsic motivators include personal values and the desire to keep oneself and others safe, while extrinsic motivators may involve rewards, recognition, or compliance with regulations. Understanding these motivators can help organizations design more engaging and effective training programs.