Air Pollution and Personal Safety: The Connection
In today's world, the air we breathe is becoming increasingly polluted, and this has a direct impact on our personal safety and health. Air pollution is not just an environmental issue; it is a pressing public health concern that affects everyone, from city dwellers to rural residents. The connection between air quality and our well-being is both profound and alarming. As we delve into this topic, we will uncover the various types of pollutants, their sources, and the serious health risks they pose. But it doesn't stop there; we will also explore practical measures that individuals can take to safeguard their health and the role of government policies in combating this invisible threat. So, why should you care about air pollution? Because your health—and that of your loved ones—depends on it.
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, which can originate from a variety of sources. These pollutants can be classified into several categories, including particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Each of these pollutants has unique characteristics and sources. For instance, particulate matter can come from vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and even natural sources like wildfires. On the other hand, VOCs are often found in household products like paints and cleaners. Understanding these pollutants is crucial for recognizing their potential impact on our health and safety.
The health risks linked to air pollution are extensive and alarming. Exposure to these harmful substances can lead to a variety of serious health issues, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even neurological disorders. Short-term exposure can cause immediate effects such as irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, while long-term exposure can lead to chronic conditions like asthma, lung cancer, and heart disease. In fact, according to the World Health Organization, air pollution is responsible for millions of premature deaths each year. It's a silent killer that creeps into our lives, often unnoticed until it's too late. So, what can we do to protect ourselves?
While air pollution affects everyone, certain groups are particularly vulnerable to its adverse effects. Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions face heightened risks. For example, children's developing lungs and immune systems make them especially susceptible to the dangers of poor air quality. They breathe more air relative to their body weight compared to adults, which means they inhale more pollutants. Similarly, older adults often have underlying health issues that can be exacerbated by exposure to polluted air. Understanding why these populations are at greater risk is essential for developing targeted interventions and protective measures.
Protecting our children from air pollution is a top priority. Their bodies are still growing, and exposure to harmful pollutants can lead to long-lasting health issues. Studies have shown that children exposed to high levels of air pollution are at a greater risk for developing respiratory diseases and even cognitive impairments. As parents and caregivers, it's crucial to be aware of air quality levels, especially on days when pollution is high. Keeping children indoors during these times, using air purifiers, and advocating for cleaner air initiatives are just a few ways we can shield them from harm.
The elderly population faces unique challenges when it comes to air pollution. Many older adults have pre-existing health conditions such as heart disease or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which can be aggravated by poor air quality. Additionally, their immune systems may not respond as effectively to pollutants, making them more vulnerable. It's essential for caregivers and family members to monitor air quality and take preventative measures, such as ensuring good ventilation and reducing exposure to outdoor pollutants.
Fortunately, there are several steps individuals can take to protect themselves from the dangers of air pollution. Here are a few practical measures:
- Stay Informed: Regularly check air quality indexes (AQI) in your area to stay aware of pollution levels.
- Limit Outdoor Activities: On days when air quality is poor, try to stay indoors, particularly during peak pollution hours.
- Use Air Purifiers: Investing in high-quality air purifiers can significantly improve indoor air quality.
- Advocate for Change: Support local and national initiatives aimed at reducing air pollution.
Effective air quality management requires robust regulations and policies. Governments worldwide have implemented various strategies to combat air pollution and protect public health. Legislation such as the Clean Air Act in the United States has set strict limits on emissions from industries and vehicles, significantly improving air quality over the years. However, continuous efforts are needed to adapt to new challenges and emerging pollutants.
Global efforts to combat air pollution include international treaties and agreements, such as the Paris Agreement. These collaborations are vital in addressing air quality issues that transcend borders. By working together, countries can share best practices, technologies, and strategies to reduce pollution levels and protect the health of their citizens.
Community-level initiatives play a crucial role in improving air quality. Local governments and organizations can implement programs aimed at reducing emissions, promoting public transportation, and encouraging green spaces. Community awareness campaigns can also educate residents about the importance of clean air and how they can contribute to improving air quality in their neighborhoods. When communities come together, they can create significant changes that lead to healthier environments for everyone.
Q: What are the most common sources of air pollution?
A: Common sources include vehicle emissions, industrial discharges, agricultural activities, and household products.
Q: How can I check the air quality in my area?
A: You can check local air quality indexes online or through weather apps that provide real-time data.
Q: What can I do if I’m exposed to poor air quality?
A: Limit outdoor activities, stay indoors during high pollution days, and use air purifiers to improve indoor air quality.
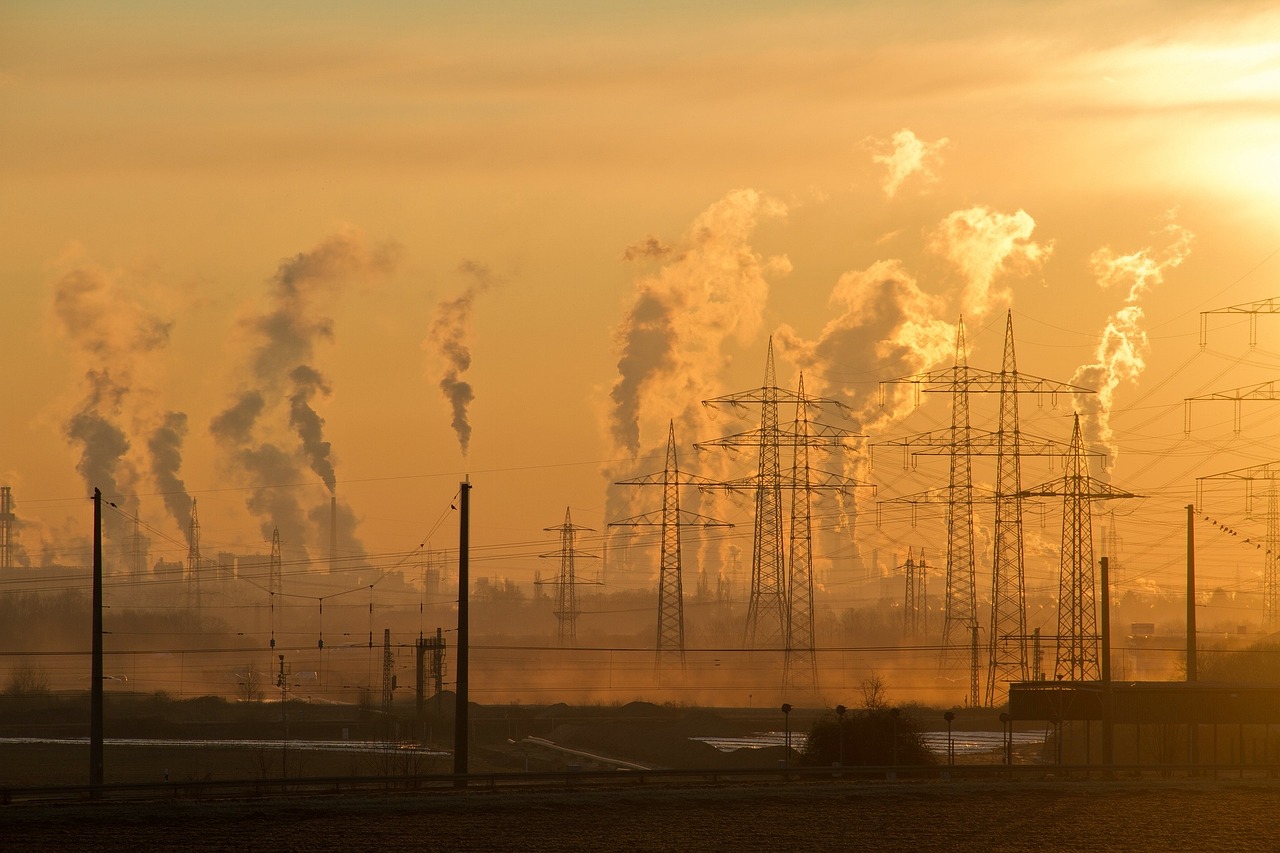

Understanding Air Pollution
This article explores the intricate relationship between air pollution and personal safety, highlighting the health risks associated with poor air quality and suggesting measures to mitigate these dangers.
Air pollution is a pressing issue that affects the quality of the air we breathe and, consequently, our overall health. It refers to the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, which can arise from a variety of sources. These substances, known as pollutants, can be either natural or man-made. Understanding the types of pollutants and their origins is crucial in grasping the full impact of air pollution on our lives.
Pollutants can be broadly categorized into two types: primary pollutants and secondary pollutants. Primary pollutants are those that are emitted directly into the air from sources like vehicles, factories, and wildfires. Examples include:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by burning fossil fuels.
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2): Emitted from power plants and industrial facilities, it can lead to acid rain.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Produced from vehicle exhaust and industrial processes, contributing to smog.
On the other hand, secondary pollutants form when primary pollutants react in the atmosphere. A common example is ozone (O3), which is created when sunlight reacts with pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides. This can lead to smog, especially in urban areas during hot weather.
The sources of air pollution are diverse and can be grouped into several categories:
| Source Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Transportation | Cars, trucks, buses, and motorcycles |
| Industry | Manufacturing plants, refineries, and power stations |
| Agriculture | Pesticides, fertilizers, and livestock waste |
| Residential | Heating systems, cooking, and household chemicals |
| Natural Sources | Wildfires, volcanic eruptions, and dust storms |
As you can see, air pollution is not just an urban problem; it affects rural areas as well, especially due to agricultural practices and natural events. The complexity of air pollution lies in its sources and the various chemical reactions that can occur in the atmosphere, leading to different types of pollutants. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing effective strategies to combat air pollution and protect our health.
In summary, air pollution is a multifaceted issue that arises from various sources, both natural and human-made. By recognizing the types of pollutants and their origins, we can better appreciate the importance of taking action to improve air quality and safeguard our personal safety.
Exposure to air pollutants can lead to serious health issues, including respiratory diseases and cardiovascular problems. This section discusses the short-term and long-term health effects on individuals.
Certain groups, such as children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing health conditions, are more susceptible to the effects of air pollution. This part examines why these populations are at greater risk.
Children's developing lungs and immune systems make them particularly vulnerable to air pollution. This subsection highlights the importance of protecting children from poor air quality.
Older adults often face increased health risks from air pollution due to underlying health issues. This subsection discusses the specific impacts on elderly populations.
Individuals can take various steps to protect themselves from the dangers of air pollution. This section outlines practical measures to reduce exposure and enhance personal safety.
Effective air quality management requires robust regulations and policies. This section reviews current legislation aimed at reducing air pollution and protecting public health.
Global efforts to combat air pollution include international treaties and agreements. This part explores the significance of these collaborations in addressing air quality issues.
Community-level initiatives play a crucial role in improving air quality. This subsection discusses how local actions can lead to significant changes in air pollution levels.
Here are some common questions regarding air pollution and personal safety:
- What are the main causes of air pollution? Air pollution is caused by various factors, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, agricultural activities, and natural events.
- How can I protect myself from air pollution? You can reduce exposure by staying indoors on high pollution days, using air purifiers, and wearing masks when necessary.
- Are there specific health risks associated with air pollution? Yes, air pollution can lead to respiratory issues, heart disease, and other serious health problems.

Health Risks Associated with Air Pollution
Air pollution is not just a buzzword thrown around in environmental discussions; it's a **serious health hazard** that affects millions worldwide. Imagine stepping outside and inhaling a cocktail of harmful substances that could lead to a myriad of health issues. It's like playing a game of Russian roulette with your lungs and heart. The pollutants in the air can cause both **short-term** and **long-term** health effects that can drastically alter your quality of life.
In the short term, exposure to air pollution can lead to symptoms that resemble a bad cold or flu. People may experience coughing, throat irritation, and shortness of breath. But it doesn't stop there; the long-term effects can be even more devastating. Chronic exposure to polluted air is linked to serious health conditions such as:
- Respiratory Diseases: Conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can worsen due to poor air quality.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Pollutants can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues.
- Cancer: Certain air pollutants are classified as carcinogens, increasing the risk of lung cancer.
- Neurological Issues: Emerging research suggests a link between air pollution and cognitive decline, particularly in older adults.
These health risks are not just statistics; they represent real consequences for individuals and families. For instance, a person with asthma might find it increasingly difficult to breathe on days when air quality is poor, leading to missed work or school. Similarly, individuals with heart conditions may face heightened risks during air pollution episodes, resulting in hospital visits or worse.
Furthermore, air pollution doesn't just affect those with pre-existing conditions; it can also have a **profound impact on the general population**. Studies have shown that even healthy individuals can experience decreased lung function and increased respiratory symptoms when exposed to high levels of air pollution over time. It's like trying to run a marathon with a weight tied to your back; eventually, it takes its toll.
To better understand the magnitude of these health risks, consider the following table that outlines various health conditions linked to air pollution:
| Health Condition | Short-term Effects | Long-term Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Asthma | Coughing, wheezing | Increased attacks, chronic asthma |
| Heart Disease | Chest pain, palpitations | Heart attacks, heart failure |
| Lung Cancer | None specific | Increased risk of lung cancer |
| Neurological Disorders | Headaches, dizziness | Cognitive decline, dementia |
It's crucial to recognize that these health risks are **interconnected**. For example, a person suffering from asthma may also have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular problems. Thus, the implications of air pollution extend far beyond individual health; they ripple throughout families and communities, affecting productivity, healthcare costs, and overall well-being.
In conclusion, the health risks associated with air pollution are both alarming and preventable. Awareness and action are essential in combating these dangers. As we move forward, it’s vital to advocate for cleaner air and support initiatives aimed at improving air quality, not just for ourselves, but for future generations.
Q: What are the main sources of air pollution?
A: Major sources include vehicle emissions, industrial discharges, burning of fossil fuels, and agricultural activities.
Q: How can I protect myself from air pollution?
A: Stay indoors on high pollution days, use air purifiers, and wear masks when necessary. Additionally, support policies aimed at improving air quality.
Q: Are children more affected by air pollution?
A: Yes, children are particularly vulnerable due to their developing lungs and immune systems, making it crucial to protect them from poor air quality.

Vulnerable Populations
When we talk about air pollution, it's not just a vague concept that affects everyone equally. In reality, certain groups of people are much more vulnerable to the harmful effects of polluted air. Think of it like a game of dodgeball; while some players are quick enough to evade the ball, others are left exposed and at risk. In this case, the 'balls' are the pollutants, and the 'players' include children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Children are particularly at risk due to their developing bodies. Their lungs are still growing, and their immune systems are not yet fully equipped to handle the onslaught of toxins found in polluted air. Exposure can lead to serious health issues such as asthma, reduced lung function, and even developmental delays. It’s like giving a plant too much fertilizer; instead of thriving, it struggles to survive. Protecting our children from poor air quality is not just a precaution; it's a necessity for their healthy development.
On the other end of the spectrum, we have the elderly. As people age, their bodies become more susceptible to various health issues, and air pollution can exacerbate these problems. For older adults, even minor pollutants can trigger serious respiratory problems or worsen existing conditions like heart disease. Imagine a house of cards; if one card is removed, the whole structure can collapse. In this case, the health of elderly individuals can be precariously balanced, and air pollution can easily tip the scales.
Furthermore, individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are also at a heightened risk. For these individuals, polluted air can act as a trigger, leading to flare-ups or complications that might otherwise have been manageable. The impact of air pollution on these vulnerable populations is not just a statistic; it's a real threat that can lead to increased hospital visits, long-term health complications, and even premature death.
To better understand the disparities in vulnerability, here’s a quick overview of how different populations are affected by air pollution:
| Population Group | Health Risks | Reasons for Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|
| Children | Asthma, developmental issues | Developing lungs and immune systems |
| The Elderly | Respiratory and cardiovascular diseases | Pre-existing health conditions |
| Individuals with Health Conditions | Increased severity of existing illnesses | Compromised health status |
In conclusion, understanding the vulnerabilities of these populations is crucial for implementing effective strategies to protect them from the dangers of air pollution. By recognizing who is most at risk, we can take targeted actions to improve air quality and safeguard the health of our communities.
- What are the main sources of air pollution? Air pollution can come from various sources including vehicle emissions, industrial discharges, and natural events like wildfires.
- How can I protect my family from air pollution? You can stay indoors on high pollution days, use air purifiers, and ensure proper ventilation in your home.
- Are there specific air quality standards? Yes, many countries have established air quality standards to protect public health, including limits on pollutants like PM2.5 and ozone.

Children and Air Quality
When it comes to air quality, children are among the most vulnerable populations. Their bodies are still developing, and their lungs are not yet fully formed, which makes them particularly sensitive to the harmful effects of pollutants. Imagine their lungs as sponges, soaking up everything in their environment, including toxic particles that can lead to serious health issues. Studies have shown that children exposed to high levels of air pollution are at a greater risk for respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis, which can hinder their ability to play, learn, and thrive.
Moreover, children tend to spend more time outdoors, engaging in activities that increase their exposure to polluted air. Whether they're riding their bikes, playing in the park, or simply walking to school, they are constantly inhaling air that may be filled with harmful substances. This is particularly concerning in urban areas where traffic and industrial activities contribute significantly to air pollution levels. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has identified several pollutants that can have detrimental effects on children's health, including:
- Particulate Matter (PM): Tiny particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): Emitted from vehicles and industrial processes, it can irritate the respiratory system.
- Ozone (O3): A harmful gas that can exacerbate asthma and other lung conditions.
It's not just about immediate effects; the long-term consequences of poor air quality can be staggering. Research indicates that children exposed to high levels of air pollution may face developmental delays, cognitive impairments, and an increased risk of chronic illnesses later in life. This is alarming because it means that the air we breathe today can shape the health of future generations.
So, what can we do to protect our children? First, it’s essential to monitor air quality reports and limit outdoor activities on days when pollution levels are high. Schools and parents can work together to create a safe environment by implementing measures such as:
- Encouraging indoor activities during peak pollution times.
- Utilizing air purifiers in homes and classrooms.
- Advocating for cleaner transportation options, like biking or walking, to reduce vehicular emissions.
In conclusion, safeguarding our children from the adverse effects of air pollution is not just a personal responsibility; it’s a societal imperative. By raising awareness and taking action, we can create a healthier environment for the youngest members of our community, ensuring they can breathe easy today and in the future.
Q: Why are children more affected by air pollution than adults?
A: Children's lungs and immune systems are still developing, making them more susceptible to the harmful effects of air pollutants.
Q: What are some common pollutants that affect children's health?
A: Common pollutants include particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone, which can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems.
Q: How can I protect my child from air pollution?
A: Monitor air quality reports, limit outdoor activities during high pollution days, and use air purifiers in your home.

The Elderly's Health Concerns
As we age, our bodies become more vulnerable to a variety of health issues, and air pollution is no exception. The elderly often face a unique set of challenges when it comes to their health, particularly as it relates to the quality of the air they breathe. With weakened immune systems and pre-existing health conditions, older adults can experience exacerbated effects from pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. These pollutants can lead to severe respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and even cognitive decline.
Imagine your lungs as a sponge; over time, they can become saturated with harmful substances, making it harder for them to function effectively. This is particularly concerning for the elderly, whose lungs may already be compromised. Studies have shown that exposure to poor air quality can increase the risk of hospital admissions for respiratory issues, heart attacks, and strokes among older adults. In fact, a recent study highlighted that seniors living in areas with high pollution levels are significantly more likely to experience these health crises compared to those in cleaner environments.
Moreover, the elderly are often less mobile, which limits their ability to escape polluted areas. For instance, they may not have the energy or resources to travel to parks or other green spaces where air quality is better. This creates a vicious cycle where they are continuously exposed to harmful pollutants, further deteriorating their health. Additionally, many older adults rely on medications that can interact negatively with air pollution, compounding their health risks.
To illustrate the impact of air pollution on the elderly, consider the following table that summarizes key health risks:
| Health Issue | Effect of Air Pollution |
|---|---|
| Respiratory Diseases | Increased risk of asthma, chronic bronchitis, and pneumonia. |
| Cardiovascular Problems | Higher likelihood of heart attacks and strokes. |
| Cognitive Decline | Potential for accelerated dementia and memory issues. |
As we can see, the stakes are incredibly high. It's crucial for families and caregivers to be aware of these risks and take proactive measures to protect their elderly loved ones. Simple actions, such as using air purifiers indoors, monitoring air quality reports, and minimizing outdoor activities on days with high pollution, can make a significant difference. By being informed and proactive, we can help shield our seniors from the hidden dangers lurking in the air.
- What are the primary sources of air pollution affecting the elderly?
Common sources include vehicle emissions, industrial discharges, and even household products like cleaning supplies.
- How can I monitor air quality in my area?
You can use various apps and websites that provide real-time air quality data, making it easier to plan outdoor activities.
- What steps can families take to protect their elderly loved ones?
Consider using air purifiers, keeping windows closed on high pollution days, and encouraging indoor activities when air quality is poor.

Preventive Measures for Personal Safety
When it comes to air pollution, taking proactive steps to safeguard your health is essential. It's not just about avoiding smoggy days; it’s about making informed choices every day. One of the first things you can do is to stay informed about the air quality in your area. Websites and mobile apps can provide real-time data on air pollution levels, allowing you to plan your outdoor activities accordingly. Think of it like checking the weather before heading out—only this time, you're checking for pollutants instead of rain.
Another effective strategy is to limit outdoor activities during high pollution days. If the air quality index (AQI) indicates unhealthy levels, consider staying indoors, especially during peak traffic hours when emissions are at their highest. Indoor air can also be a concern, so ensure your home is well-ventilated. Using air purifiers can significantly reduce indoor pollutants and improve the overall air quality in your living space. It's like having a personal guardian against harmful particles.
Moreover, adopting a healthier lifestyle can bolster your body’s defenses against air pollution. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and staying hydrated can help your body cope with the effects of poor air quality. Foods like berries, leafy greens, and nuts can strengthen your immune system, making you less susceptible to the harmful effects of pollutants. Think of it as building a fortress—every healthy choice adds another layer of protection.
In addition to personal efforts, community action is vital. Engage with local initiatives aimed at reducing air pollution, such as tree-planting events or clean-up drives. Not only do these activities improve your environment, but they also foster a sense of community and shared responsibility. Together, we can create a cleaner, healthier atmosphere for everyone.
Lastly, advocating for policy changes can lead to long-term improvements in air quality. Support legislation that aims to reduce emissions and promote clean energy sources. Your voice matters, and collective action can lead to significant changes in how air quality is managed in your area. Just like a ripple effect, your efforts can inspire others to join the cause.
In summary, while air pollution poses serious risks to personal safety, there are numerous preventive measures you can take. By staying informed, limiting outdoor activities during high pollution days, adopting a healthy lifestyle, engaging in community actions, and advocating for policy changes, you can significantly reduce your exposure to harmful pollutants. It's all about making conscious choices that prioritize your health and safety.

Government Regulations and Policies
When it comes to tackling the daunting challenge of air pollution, play a pivotal role. These frameworks are designed to protect public health and ensure that our air remains clean and safe to breathe. From setting emission standards to promoting cleaner technologies, the effectiveness of these regulations can make a significant difference in air quality. It’s like having a sturdy umbrella on a rainy day; it may not stop the rain, but it certainly helps keep you dry!
One of the key components of air quality management is the establishment of national air quality standards. These standards are often based on scientific research and aim to limit the concentration of harmful pollutants in the air. For instance, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set guidelines for pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). These regulations are crucial because they not only protect the health of individuals but also safeguard the environment as a whole.
Moreover, local governments also play a critical role in implementing air quality measures. They often tailor regulations to address specific regional challenges. For example, urban areas with high traffic may impose stricter vehicle emissions standards or promote public transport to reduce the number of cars on the road. This localized approach is akin to a tailor adjusting a suit to fit perfectly; it ensures that the regulations are relevant and effective for the community they serve.
To further enhance the impact of these regulations, many governments engage in public awareness campaigns. These initiatives educate citizens about the importance of air quality and encourage them to take part in reducing pollution. For example, communities are often encouraged to participate in “car-free days” or adopt more sustainable practices like recycling and using energy-efficient appliances. By fostering a sense of community responsibility, these campaigns can lead to lasting changes in behavior.
International cooperation is also essential in addressing air pollution. Many countries have come together to form global agreements aimed at reducing airborne contaminants. The Paris Agreement, for instance, seeks to limit greenhouse gas emissions globally, which indirectly benefits air quality. These agreements are like a group project in school; when everyone contributes, the outcome is much better than if only a few people do the work.
In summary, government regulations and policies are fundamental in the fight against air pollution. They help set standards, promote public awareness, and encourage international collaboration. However, the success of these measures relies not only on the government but also on the active participation of individuals and communities. Together, we can create a cleaner, healthier environment for ourselves and future generations.
- What are the main pollutants regulated by government policies?
The main pollutants typically include particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3). - How can individuals contribute to improving air quality?
Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by using public transportation, carpooling, recycling, and supporting local clean air initiatives. - What role do local governments play in air quality management?
Local governments tailor regulations to address specific regional air quality issues, implement public awareness campaigns, and promote sustainable practices. - Are there international efforts to combat air pollution?
Yes, international agreements like the Paris Agreement aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality on a global scale.

International Agreements
When it comes to tackling the ever-growing issue of air pollution, play a pivotal role in shaping policies and fostering cooperation among nations. Think of these agreements as a global handshake, where countries come together to acknowledge that air pollution knows no borders and that collective action is essential for meaningful change. One of the most notable agreements is the Paris Agreement, which, while primarily focused on climate change, also addresses air quality by promoting the reduction of greenhouse gases that contribute to pollution.
These agreements are not just lofty ideals; they translate into real-world actions that can significantly improve air quality. For instance, the Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution (CLRTAP) is a prime example of how international collaboration can lead to actionable policies. Established in 1979, CLRTAP aims to limit and reduce air pollution by encouraging countries to work together to cut emissions that can travel long distances across borders. This agreement has led to several protocols targeting specific pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which are notorious for their harmful effects on health and the environment.
Furthermore, international agreements often include provisions for monitoring and reporting air quality data. This transparency is crucial, as it holds countries accountable for their emissions and encourages them to adopt cleaner technologies. For instance, the Global Burden of Disease Study has provided invaluable data that informs policy decisions and helps governments understand the health impacts of air pollution. When countries can see the tangible effects of their pollution on health, it becomes a powerful motivator for change.
However, achieving consensus among nations can be challenging. Different countries have varying levels of industrialization, economic resources, and public health priorities. This disparity can lead to disagreements on the best approaches to take. Nevertheless, the importance of collaborative efforts cannot be overstated. By sharing technology, resources, and knowledge, countries can develop innovative solutions to combat air pollution.
In conclusion, international agreements serve as a vital framework for addressing air pollution on a global scale. They foster collaboration, promote accountability, and drive countries towards cleaner air. As we move forward, it is essential for nations to remain committed to these agreements and continuously seek ways to enhance their effectiveness. After all, clean air is not just a local issue; it’s a global responsibility.

Local Initiatives and Community Action
When it comes to tackling air pollution, local initiatives and community action can be game changers. These grassroots movements often arise from a shared concern for health and the environment, and they can lead to significant improvements in air quality. Imagine a neighborhood coming together, united by a common goal: to breathe cleaner air. This is not just a dream; it’s happening in communities around the world!
One of the most effective ways communities can combat air pollution is through awareness campaigns. These campaigns educate residents on the sources and effects of air pollution, empowering them to make informed choices. For instance, a local group might organize workshops on the importance of reducing car emissions by promoting public transportation or carpooling. Such initiatives not only raise awareness but also foster a sense of responsibility among community members.
Moreover, community gardens and green spaces are popping up in urban areas, serving as both a sanctuary for residents and a method to improve air quality. Plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, making these green areas crucial in the fight against pollution. By creating more parks and gardens, communities can literally breathe easier. In fact, studies have shown that urban greenery can significantly reduce air pollutants like nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter.
Another impactful action is the establishment of local air quality monitoring programs. These programs allow residents to track air quality levels in real-time, fostering transparency and encouraging local governments to act on pollution sources. By engaging citizens in the monitoring process, communities can advocate for necessary changes, such as stricter emissions regulations for local industries.
In addition to these initiatives, community events like clean-up drives and tree-planting days are excellent ways to mobilize residents. Not only do these events beautify neighborhoods, but they also promote environmental stewardship. When people physically participate in improving their surroundings, they develop a deeper connection to their community and its health.
Here are a few examples of successful local initiatives:
| Community | Initiative | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | Urban Greening Program | Increased tree canopy cover by 20%, reducing urban heat and improving air quality. |
| New York City | NYC CoolRoofs | Coated over 10 million square feet of rooftops, lowering city temperatures and reducing energy consumption. |
| Los Angeles | Clean Air Action Plan | Implemented measures to reduce emissions from transportation and industrial sources, resulting in a 30% decrease in smog levels. |
In conclusion, community action is vital in the fight against air pollution. By coming together, residents can create a ripple effect that not only enhances their immediate environment but also contributes to a healthier planet. Every small step counts, and when communities unite, they can achieve remarkable results. After all, the air we breathe is a shared resource, and it’s up to all of us to protect it.
Q1: How can I get involved in local air quality initiatives?
A1: You can start by researching local environmental groups or community organizations. Many cities have volunteer opportunities for clean-up events, tree planting, and awareness campaigns. Joining these initiatives is a great way to contribute!
Q2: What are the benefits of planting trees in urban areas?
A2: Trees improve air quality by absorbing pollutants, providing shade, and cooling the environment. They also enhance community aesthetics and promote biodiversity.
Q3: How can I advocate for better air quality in my community?
A3: You can attend local government meetings, participate in community forums, and collaborate with local advocacy groups. Raising awareness and pushing for policy changes are crucial steps in advocating for cleaner air.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is air pollution?
Air pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere, which can come from various sources, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and natural events like wildfires. These pollutants can have serious health impacts on individuals and the environment.
- How does air pollution affect personal safety?
Air pollution poses significant risks to personal safety by leading to health issues such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even mental health impacts. Poor air quality can exacerbate existing health conditions and increase susceptibility to illnesses.
- Who is most vulnerable to air pollution?
Certain groups are more susceptible to the effects of air pollution, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions. Their developing or weakened immune systems make them particularly at risk for serious health effects.
- What can individuals do to protect themselves from air pollution?
To reduce exposure to air pollution, individuals can take practical measures such as staying indoors on high pollution days, using air purifiers, wearing masks when necessary, and advocating for cleaner air policies in their communities.
- Are there regulations in place to combat air pollution?
Yes, there are various government regulations and policies aimed at reducing air pollution and protecting public health. These include emission standards for industries, vehicle regulations, and initiatives to promote cleaner energy sources.
- What role do international agreements play in addressing air pollution?
International agreements are crucial in the fight against air pollution as they facilitate collaboration between countries to implement strategies that reduce emissions and improve air quality on a global scale. Treaties like the Paris Agreement aim to address climate change and its impact on air quality.
- How can local communities make a difference in air quality?
Local communities can significantly impact air quality through initiatives such as tree planting, promoting public transportation, and organizing awareness campaigns. Community action can lead to meaningful changes that improve air quality and public health.